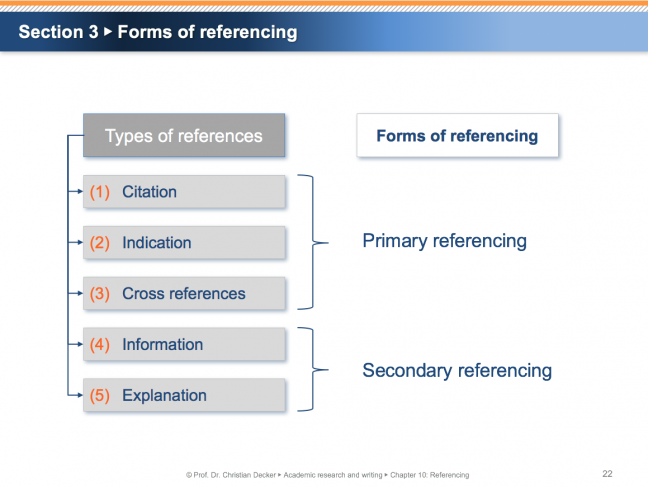
The academic principle of inter-subjective comprehensibility requires the traceability of thoughts and conclusions. Thus, academic research and writing is characterised by meticulous referencing. Style guides or citation guidelines define the applicable rules of referencing. Generally, five different types of references are distinguished: citation, indication, cross references, information and explanation. The two major types of referencing techniques are parenthetical referencing and footnote referencing. Parenthetical referencing can be performed by the use of the “author-date method” (“Harvard style”, “APA style”) or the “author-title method” (“author-page method”, “MLA style”). Parenthetical referencing requires an unstructured bibliography or an unstructured list of references. Footnote referencing with full information allows for a structured bibliography or a structured list of references.
Link to e-learning videos: Overview of chapter 10